区别:Python json.load()和json.loads()读取JSON
作者:admin 时间:2021-12-27 9:53:53 浏览:本文介绍如何使用 Python json.load()和json.loads()方法从文件和字符串读取 JSON 数据。
使用json.load()和json.loads()方法,你可以将 JSON 编码/格式化数据转换为 Python 类型,此过程称为 JSON 解码。Python 内置模块 json 提供了以下两种方法来解码 JSON 数据。
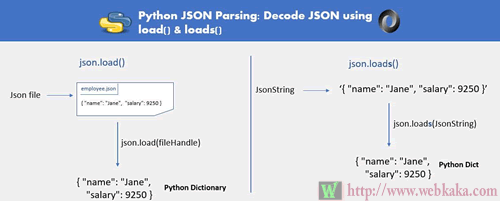
使用load和loads解析Python JSON
要从 URL 或文件解析 JSON,请使用json.load(),对于带有 JSON 内容的解析字符串,请使用json.loads()。
json.load()和json.loads()的语法
我们可以使用load()和loads()方法进行许多 JSON 解析操作。首先,了解它的语法和参数,然后我们将一一介绍其用法。
json.load()的语法
json.load(fp, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)
json.loads()的语法
json.loads(s, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)
所有参数在这两种方法中都具有相同的含义。
使用的参数:
json.load()用于从文件中读取 JSON 文档, 而json.loads()用于将 JSON String 文档转换为 Python 字典。- fp 用于读取包含 JSON 文档的文本文件、二进制文件或 JSON 文件的文件指针。
- object_hook 是可选函数,将使用任何对象文字解码的结果调用。Python 内置的 json 模块只能处理具有直接 JSON 等效项的原语类型(例如,字典、列表、字符串、数字、无等)。但是当你想将 JSON 数据转换成自定义的 Python 类型时,我们需要实现自定义解码器并将其作为对象传递object_hook给一个
load()方法,这样我们就可以获得自定义的 Python 类型而不是字典。 - object_pairs_hook 是一个可选函数,它将使用任何对象字面量的结果调用,该结果是用有序的对列表解码的。object_pairs_hook 将使用的返回值 代替 Python 字典。此功能还可用于实现自定义解码器。如果 object_hook 也定义了, object_pairs_hook 则优先。
- parse_float 是可选参数,但如果指定,将使用要解码的每个 JSON 浮点数和整数的字符串调用。默认情况下,这等效于float(num_str)。
- parse_int 如果指定,它将使用要解码的每个 JSON int 的字符串调用。默认情况下,这等效于int(num_str).
我们将详细了解所有这些参数的使用。
json.load() 从文件中读取 JSON 数据并将其转换为字典
使用一种json.load()方法,我们可以从文本、JSON或二进制文件中读取 JSON 数据。该json.load()方法以 Python 字典的形式返回数据。稍后我们使用这个字典来访问和操作我们的应用程序或系统中的数据。
解码时JSON和Python实体之间的映射
请参考下面的转换表,该表是json.load()和json.loads()方法在解码时使用的转换表。
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int & float-derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
现在,让我们看看这个例子。在这个例子中,我正在读取我硬盘上的“ developer.json ”文件。此文件包含以下 JSON 数据。
{
"name": "Kaka",
"salary": 9000,
"skills": [
"Raspberry pi",
"Machine Learning",
"Web Development"
],
"email": "Kaka@webkaka.com",
"projects": [
"Python Data Mining",
"Python Data Science"
]
}
示例
import json
print("Started Reading JSON file")
with open("developer.json", "r") as read_file:
print("Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary")
developer = json.load(read_file)
print("Decoded JSON Data From File")
for key, value in developer.items():
print(key, ":", value)
print("Done reading json file")
输出
Started Reading JSON file
Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary
Decoded JSON Data From File
name : kaka
salary : 9000
skills : ['Raspberry pi', 'Machine Learning', 'Web Development']
email : Kaka@webkaka.com
projects : ['Python Data Mining', 'Python Data Science']
Done reading json file
使用键名直接访问 JSON 数据
使用以下代码如果要直接访问 JSON 密钥而不是从文件中迭代整个 JSON。
import json
print("Started Reading JSON file")
with open("developer.json", "r") as read_file:
print("Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary")
developer = json.load(read_file)
print("Decoding JSON Data From File")
print("Printing JSON values using key")
print(developer["name"])
print(developer["salary"])
print(developer["skills"])
print(developer["email"])
print("Done reading json file")
输出
Started Reading JSON file
Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary
Decoding JSON Data From File
Printing JSON values using key
kaka
9000
['Raspberry pi', 'Machine Learning', 'Web Development']
Kaka@webkaka.com
Done reading json file
你可以使用上述相同的方式从文本、json 或二进制文件中读取 JSON 数据。
json.loads() 将 JSON 字符串转换为字典
有时我们会收到字符串格式的 JSON 响应。因此,要在我们的应用程序中使用它,我们需要将 JSON 字符串转换为 Python 字典。使用该json.loads()方法,我们可以将包含 JSON 文档的原生 String、byte 或 bytearray 实例反序列化为 Python 字典。我们可以参考文章开头提到的转换表。
import json
developerJsonString = """{
"name": "kaka",
"salary": 9000,
"skills": [
"Raspberry pi",
"Machine Learning",
"Web Development"
],
"email": "kaka@webkaka.com",
"projects": [
"Python Data Mining",
"Python Data Science"
]
}
"""
print("Started converting JSON string document to Python dictionary")
developerDict = json.loads(developerJsonString)
print("Printing key and value")
print(developerDict["name"])
print(developerDict["salary"])
print(developerDict["skills"])
print(developerDict["email"])
print(developerDict["projects"])
print("Done converting JSON string document to a dictionary")
输出
Started converting JSON string document to Python dictionary
Printing key and value
jane doe
9000
['Raspberry pi', 'Machine Learning', 'Web Development']
JaneDoe@pynative.com
['Python Data Mining', 'Python Data Science']
Done converting JSON string document to a dictionary
解析和检索嵌套的 JSON 数组键值
假设你有一个如下所示的 JSON 响应:
developerInfo = """{
"id": 23,
"name": "Kaka",
"salary": 9000,
"email": "kaka@webkaka.com",
"experience": {"python":5, "data Science":2},
"projectinfo": [{"id":100, "name":"Data Mining"}]
}
"""
例如,你想从开发人员信息 JSON 数组中检索项目名称,以了解他/她正在从事的项目。现在让我们看看如何读取嵌套的 JSON 数组键值。
在此示例中,我们使用了开发人员信息 JSON 数组,该数组具有作为嵌套 JSON 数据的项目信息和经验。
import json
print("Started reading nested JSON array")
developerDict = json.loads(developerInfo)
print("Project name: ", developerDict["projectinfo"][0]["name"])
print("Experience: ", developerDict["experience"]["python"])
print("Done reading nested JSON Array")
输出
Started reading nested JSON array
Project name: Data Mining
Experience: 5
Done reading nested JSON Array
将 JSON 加载到 OrderedDict 中
OrderedDict 可以用作 JSON 的输入。我的意思是,当你将 JSON 转储到文件或字符串中时,我们可以将 OrderedDict 传递给它。
但是,当我们想要维护顺序时,我们将 JSON 数据加载回 OrderedDict 以便我们可以保持文件中键的顺序。
现在让我们看看例子。
import json
from collections import OrderedDict
print("Ordering keys")
OrderedData = json.loads('{"John":1, "Emma": 2, "Ault": 3, "Brian": 4}', object_pairs_hook=OrderedDict)
print("Type: ", type((OrderedData)))
print(OrderedData)
输出
Ordering keys
Type: <class 'collections.OrderedDict'>
OrderedDict([('John', 1), ('Emma', 2), ('Ault', 3), ('Brian', 4)])
如何使用json.load()的parse_float和parse_int
正如我已经说过的parse_float和parse_int,两者都是可选参数,但如果指定,将使用要解码的每个 JSON 浮点数和整数的字符串调用。默认情况下,这等效于float(num_str)和int(num_str)。
假设 JSON 文档包含许多浮点值,并且你希望将所有浮点值四舍五入到两位小数点。在这种情况下,我们需要定义一个自定义函数来执行你想要的任何舍入。我们可以将这样的函数传递给parse_float kwarg。
此外,如果你想对整数值执行任何操作,我们可以编写一个自定义函数并将其传递给parse_int kwarg。例如,你在 JSON 文档中收到请假天数,并且你想计算要扣除的工资。
例子
import json
def roundFloats(salary):
return round(float(salary), 2)
def salartToDeduct(leaveDays):
salaryPerDay = 465
return int(leaveDays) * salaryPerDay
print("Load float and int values from JSON and manipulate it")
print("Started Reading JSON file")
with open("developerDetails.json", "r") as read_file:
developer = json.load(read_file, parse_float=roundFloats,
parse_int=salartToDeduct)
# after parse_float
print("Salary: ", developer["salary"])
# after parse_int
print("Salary to deduct: ", developer["leavedays"])
print("Done reading a JSON file")
输出
Load float and int values from JSON and manipulate it
Started Reading JSON file
Salary: 9250.542
<class 'float'>
Salary to deduct: 3
Done reading a JSON file
在load()方法中使用JSON解码器
Python 的内置 json 模块只能处理具有直接 JSON 等效项的 Python 原语类型(例如,字典、列表、字符串、数字、None 等)。
当你执行json.load() 或 json.loads()方法时,它会返回一个 Python 字典。如果你想 将 JSON 转换为自定义 Python 对象,那么我们可以编写一个自定义 JSON 解码器并将其传递给该json.loads()方法,这样我们就可以获得自定义 Class 对象而不是字典。
下面我们来看看如何在load()方法中使用JSON解码器。在这个例子中,我们将看到如何使用load()方法的object_hook参数。
import json
from collections import namedtuple
from json import JSONEncoder
def movieJsonDecod(movieDict):
return namedtuple('X', movieDict.keys())(*movieDict.values())
# class for your reference
class Movie:
def __init__(self, name, year, income):
self.name = name
self.year = year
self.income = income
# Suppose you have this json document.
movieJson = """{
"name": "Interstellar",
"year": 2014,
"income": 7000000
}"""
# Parse JSON into an Movie object
movieObj = json.loads(movieJson, object_hook=movieJsonDecod)
print("After Converting JSON into Movie Object")
print(movieObj.name, movieObj.year, movieObj.income)
输出
After Converting JSON into Movie Object
Interstellar 2014 7000000
总结
本文介绍了Python json.load()和json.loads()读取JSON的区别。通过本文,你将学会如何使用 Python json.load()和json.loads()方法从文件和字符串读取 JSON 数据。